
Here is an example of a service command which will be scheduled on 2 available nodes: Service: A service specifies the container image and the number of replicas.Worker Nodes: These nodes collect and run tasks from manager nodes.Manager nodes can also perform the duties of worker nodes. Manager Nodes: These nodes receive service definitions from the user, and dispatch work to worker nodes.In Swarm mode, you orchestrate services, instead of running container commands. Swarm: a cluster of nodes (or Docker Engines).Nodes can be distributed on-premises or in public clouds. Node: A node is an instance of a Swarm.
Here are some common terms associated with Docker Swarm: The user can declaratively specify the desired state of various services to run in the Swarm cluster using YAML files. (Source: Docker Docs: Swarm mode )Īs can be seen from the figure above, the Docker Swarm architecture consists of managers and workers. In the replicated services model, ingress load balancing and internal DNS can be used to provide highly available service endpoints. Services can be replicated to run on multiple nodes. Worker nodes receive and execute tasks from the manager nodes.Ī service, which can be specified declaratively, consists of tasks that can be run on Swarm nodes. Manager nodes perform orchestration and cluster management. A Swarm cluster consists of Docker Engine deployed on multiple nodes. Kubernetes Service Mesh: A Comparison of Istio, Linkerd and Consulĭocker Engine v1.12.0 and later allow developers to deploy containers in Swarm mode.Kubernetes Multi-Tenancy Best Practices.The Definitive Guide to Kubernetes Upgrades.
Docker swarm vs kubernetes security update#
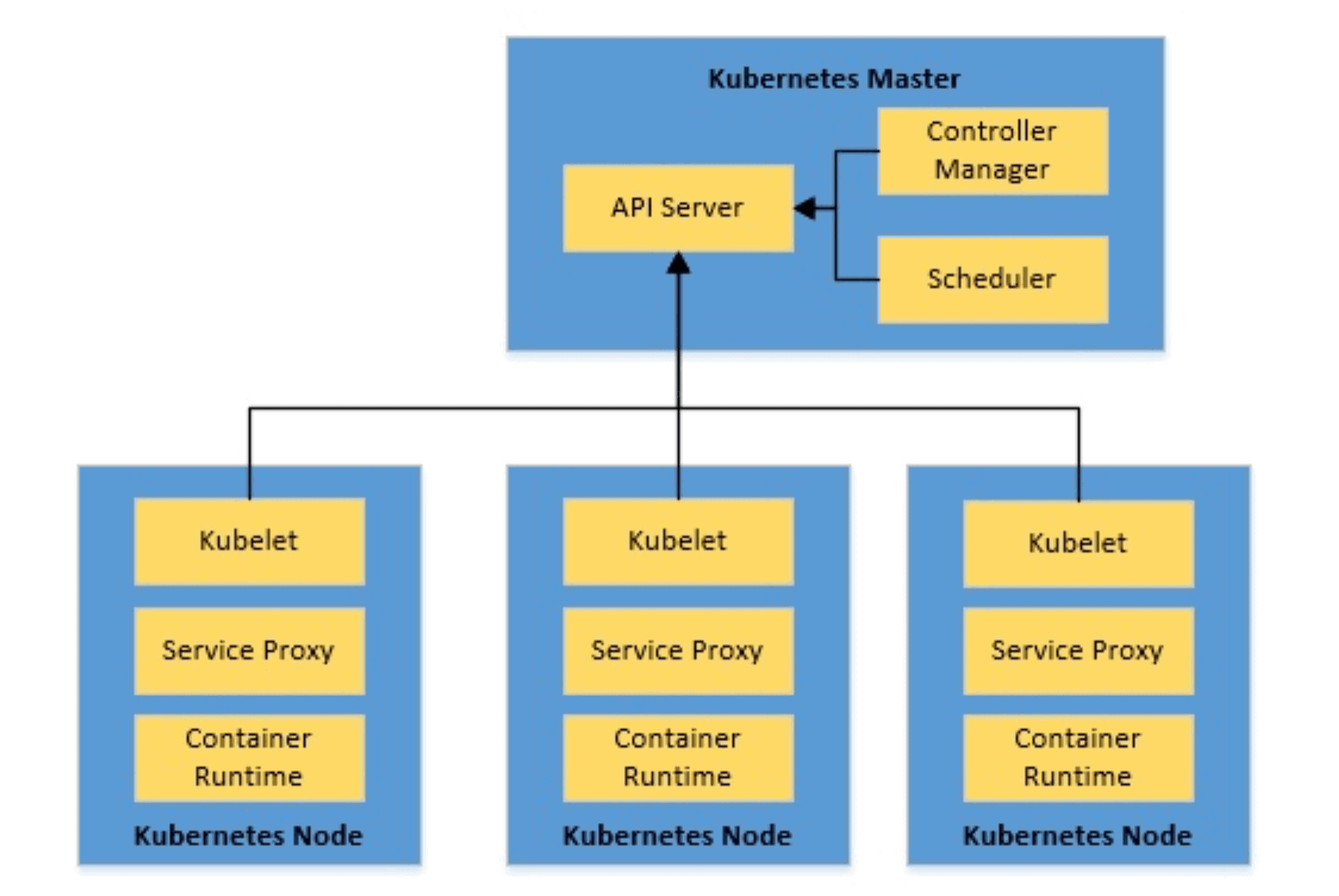
Labels: Labels are key-value pairs attached to objects and can be used to search and update multiple objects as a single set. Services are the “external face” of your container workloads. Kubernetes will set up a DNS server for the cluster that watches for new services and allows them to be addressed by name. The service will automatically round-robin requests between pods. Services: Services are endpoints that can be addressed by name and can be connected to pods using label selectors. Deployments can be used with a service tier for scaling horizontally or ensuring availability. Deployments: These building blocks can be used to create and manage a group of pods. Containers in a pod run on the same node and share resources such as filesystems, kernel namespaces, and an IP address. Pods: Kubernetes deploys and schedules containers in groups called pods. The following list provides some other common terms associated with Kubernetes: Kubelet: This component receives pod specifications from the API Server and manages pods running in the host. Scheduler: This component places the workload on the appropriate node – in this case all workloads will be placed locally on your host. Controller Manager: This component ensures that the cluster’s desired state matches the current state by scaling workloads up and down. It facilitates communication between the various components, thereby maintaining cluster health. API Server: This component is the management hub for the Kubernetes master node. etcd: This component stores configuration data which can be accessed by the Kubernetes Master’s API Server using simple HTTP or JSON API. The aster node places container workloads in user pods on worker nodes or itself. The architecture for Kubernetes, which relies on this experience, is shown below:Īs you can see from the figure above, there are a number of components associated with a Kubernetes cluster. Overview of KubernetesĪccording to the Kubernetes website, “Kubernetes is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.” Kubernetes was built by Google based on their experience running containers in production using an internal cluster management system called Borg (sometimes referred to as Omega). In this updated blog post we’ll compare Kubernetes (versions 1.5.0 and later) with Docker Swarm, also referred to as Docker Engine running in Swarm mode (versions 1.12.0 and later).






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
